In recent decades, the unprecedented levels of accessible data and computational power has led to an explosion of applications of data-driven and Machine Learning (ML) models across almost all areas, including that of hydrology and water resources. The STARS4Water project has published a report, introducing a suite of data-driven modelling tools co-developed with river basin stakeholders. These tools respond to the needs identified across the project’s seven River Basin Hubs and complement existing process-based models.
The report showcases how machine learning and advanced data techniques can leverage the increased volumes of hydrological, environmental, and socio-economic data for improved water management. Key tools developed include:
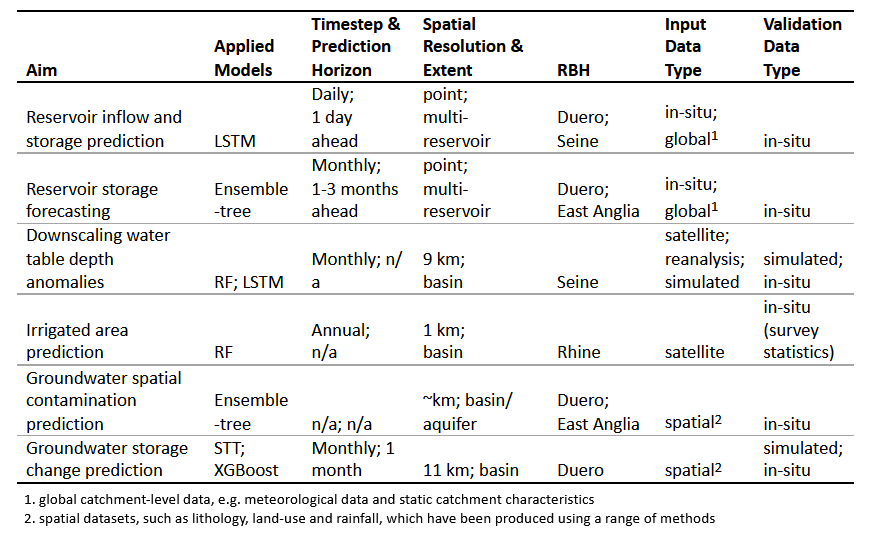
- Forecasting of reservoir storage and inflows using LSTM and ensemble-tree models to address the need for better quantitative assessments of water resources, and to support decision making for reservoir operation
- Downscaling of total water storage (GRACE, ERA5, TSMP) to estimate groundwater depth anomalies.
- Estimation of agricultural water use and irrigated areas (MODIS, Random Forest) to assess the impacts of climate change on agricultural water demand.
- Predictive mapping of groundwater quality (MLMapper) to identify contamination risks.
- Quantitative groundwater resource estimation (TSMP, STT, XGBoost) at multiple scales to refine the estimation of groundwater resources, improving understanding of groundwater impacts on droughts and low flows.
Applications across case study basins (Duero, Seine, Messara, Rhine, East Anglia) demonstrate promising results for reservoir operation, groundwater assessment, and irrigation monitoring. These approaches highlight the potential of data-driven methods to capture non-linear dynamics in a computationally efficient manner and support adaptive, resilient, and sustainable water management. With continued stakeholder collaboration, the tools can be scaled and operationalised in additional basins. Future work will focus on extending these methods and integrating them into basin-level decision support systems.
More information can be found in the following STARS4Water project Deliverable: Baron, H., Keller, V., Klotz, D., Kenne, A., Avila, L., Purnamasari, D., Martínez-Santos, P., Aguilera, H., Gómez-Escalonilla, V., Rodríguez del Rosario, M., Díaz Alcaide, S., Beckers, J., Hegdahl, T. J. (2025): Data-driver modelling tools for the STARS4Water River Basins. Horizon Europe project STARS4Water. Deliverable D3.4.




